A well-crafted HUD is more than just a functional overlay—it’s an integral part of the gaming experience. By addressing common issues like information overload, prioritizing usability over style, and implementing contextual adaptation, developers can create HUDs that enhance immersion, accessibility, and satisfaction.
Selective attention is a fundamental UX concept that directly influences how players interact with a game’s HUD. By prioritizing critical information, reducing cognitive load, and aligning with player habits, designers can create HUDs that are intuitive, immersive, and effective.
Selective attention refers to the brain’s ability to prioritize specific stimuli while ignoring irrelevant or less important details. This allows players to focus on tasks or information that are most relevant to their goals, despite being bombarded with sensory inputs from their gameplay environment.
For players, selective attention dictates how they interact with and interpret the HUD. During high-stakes moments, such as combat or timed challenges, their attention naturally narrows to focus on critical gameplay elements. This tendency highlights the need for a HUD design that directs attention effectively while avoiding unnecessary clutter.
Whether through dynamic design, intuitive tutorials, or robust customization options, the ultimate goal is to make the HUD a natural extension of the game, helping players stay engaged and informed without distraction. Balancing clarity, functionality, and adaptability is the key to a successful HUD.
1. Logical Placement of UI Elements
Position HUD components intuitively based on input methods and player behaviour. For example, action-related UI like health bars and cooldowns should be placed at the bottom or top-left, while navigation tools and objectives work best on the right side of the screen. Aligning with natural reading patterns (e.g., left-to-right for Western audiences) improves usability.
2. Contextual Visibility and Adaptability
Adapt the HUD to different gameplay scenarios. Hide unnecessary elements during low-intensity moments and emphasize critical information during combat or high-stakes gameplay. This keeps the interface clean and focused.
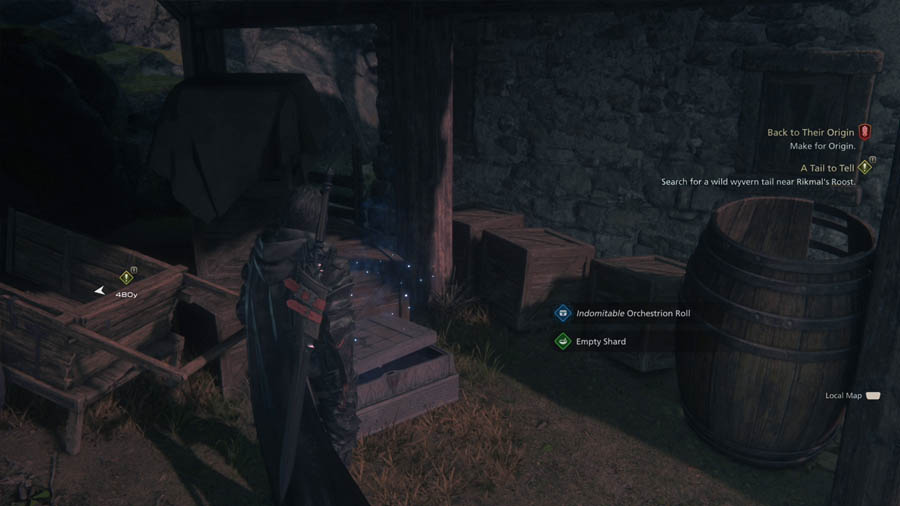
In Final Fantasy XVI, the HUD dynamically adjusts to display relevant UI elements based on the player’s current scenario, such as when exploring or discovering items. The HUD displays the character’s current objectives alongside any items they have recently discovered, ensuring players stay informed and focused on their progress. This contextual visibility ensures that players can focus on the most important information at any given moment, eliminating unnecessary clutter.
3. Intuitive Iconography
Use recognizable symbols and simple illustrations for icons to ensure players quickly understand their purpose. Avoid overly decorative designs and prioritize clarity, ensuring icons remain legible even when resized.
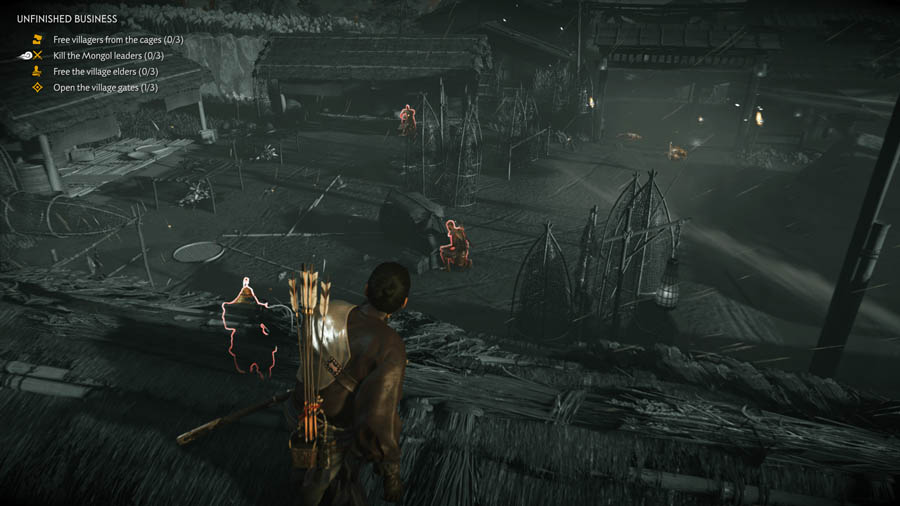

In Ghost of Tsushima, when the player enters stealth mode, the HUD dynamically displays the current objectives on the battlefield while the game’s visual style shifts to enhance immersion. This change highlights enemies, making them more visible and emphasizing key gameplay elements critical for stealth-focused strategies.
4. Dynamic UI Feedback
Add subtle animations or visual cues to draw attention to key events, such as flashing health bars when dangerously low or shaking indicators for urgent objectives. Pair these with sound effects for added accessibility and impact.
5. Onboarding and Tutorials
Introduce HUD elements and controls gradually through interactive tutorials. Provide an easily accessible reference screen for returning players to refresh their knowledge without relying on permanent HUD prompts.
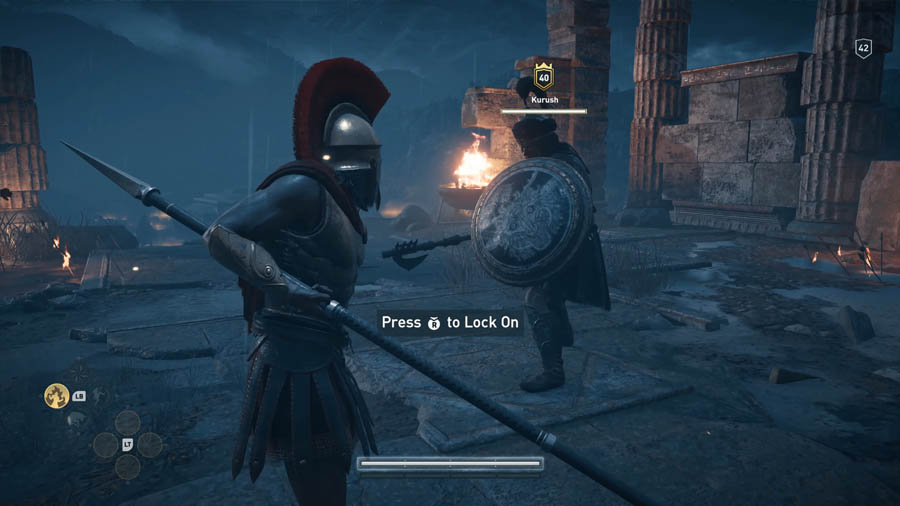
In Assassin’s Creed Odyssey, tutorial HUD controls are strategically placed near the character, within the player’s central field of vision, ensuring they are immediately noticeable and providing clear guidance on which controls to use in the moment. Additionally, the HUD dynamically displays critical UI elements, such as the enemy’s health bar, the player’s health bar, and available skills, all tailored to the current combat scenario. This design ensures players have access to essential information at a glance, enhancing both usability and gameplay flow.
6. Customization and Scalability
Offer robust customization options, enabling players to adjust the HUD based on their hardware and preferences. Scalability ensures the HUD remains functional on various screen sizes and resolutions, as well as broadening player audience through accessibility.
A well-designed HUD respects the limits of selective attention, guiding players to focus on what truly matters during gameplay. By understanding and applying these principles, developers can ensure their HUD designs complement the game’s mechanics and elevate the player’s enjoyment.
